The Lighting Global Quality Assurance Program works to ensure that solar products sold around the globe meet established quality standards for product durability, representation of product performance, and warranty. To obtain quality verification, manufacturers may submit products for testing at laboratories in the Lighting Global network.
Pico-solar products include lanterns and simple systems with a peak PV module power up to 10 watts. These small systems encompass 85% of the global cumulative sales of off-grid solar devices. Although more than 30 million quality assured off-grid solar products have been sold globally over the past eight years, the sales numbers for products that do not undergo quality verification (hence are “non-QV”) is even higher. Field observations and customer experiences indicate that non-QV products typically underperform compared to the standards established by Lighting Global.
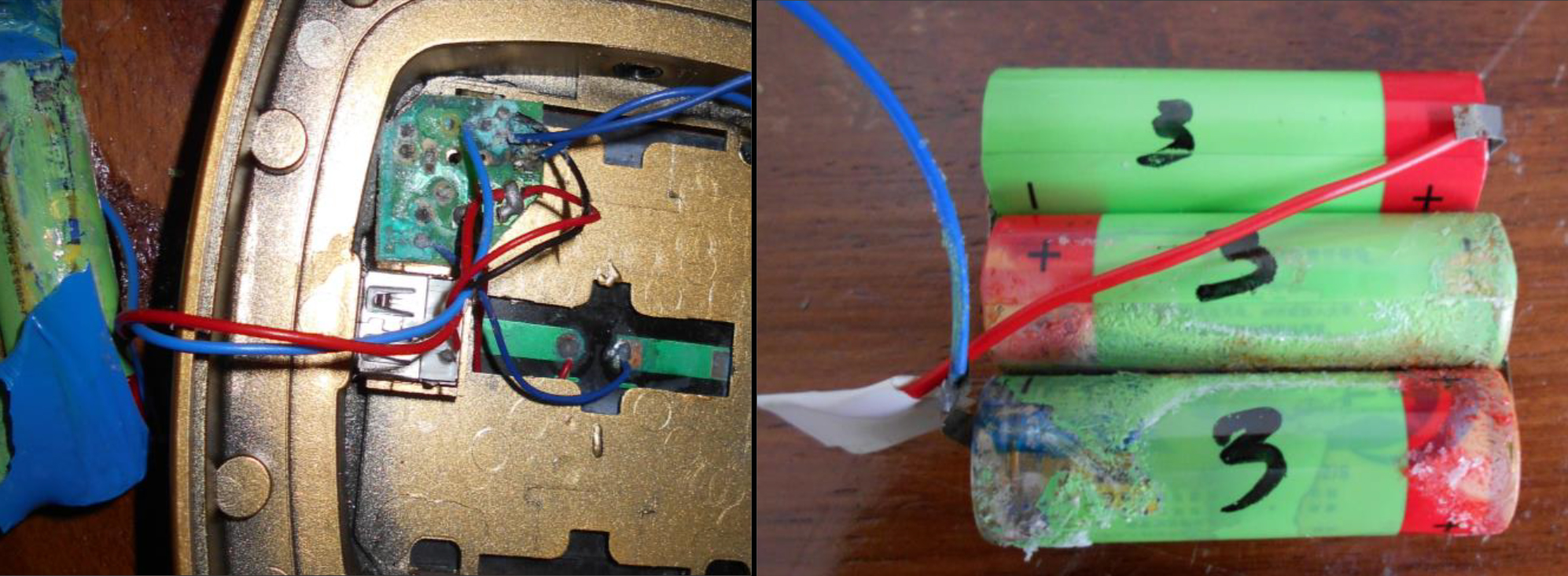
In order to ascertain the actual performance of these devices, Lighting Global laboratories recently tested 17 pico-solar non-QV products that are top-sellers in Ethiopia, Kenya, Myanmar, Nigeria and Tanzania. Products were purchased direct from market retailers.
Key results:
All 17 evaluated products failed to meet the Lighting Global Quality Standards for pico-PV products.
- 94% of the tested products fail to meet the Standards due to one or more deficiency that
affects product durability. - 88% of the tested products inaccurately advertise product performance.
- 88% of the tested products do not include a consumer-facing warranty.
- 76% of the tested products would require significant changes to product design and
components to meet the Quality Standards.
The Lighting Global Quality Assurance team issued the report this August as part of the Technical Notes series. Chris Carlsen (a Schatz Center alumnus) led the effort in collaboration with team members from CLASP, the Schatz Center, World Bank Group regional lighting programs, and the Lighting Global network of test labs.